Cat Types by Color: 10 Essential Insights for Spotting Striking Patterns
Have you ever looked into your cat’s eyes and thought about their coat’s beauty? The wide range of feline color patterns is amazing. Each cat’s coloration is unique, and understanding cat types by color helps identify these differences.
Learning about the different cat types by color can make you appreciate them more. It can also help you identify cat colors better. Whether you’re new to cats or have been a fan for years, discovering feline color patterns is exciting.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cat Color Genetics: The Foundation of Feline Hues
Understanding cat types by color begins with genetics. It’s a mix of genes that decide your cat’s coat color and pattern. Cat color genetics is complex, showing how different genes work together to create the many colors and patterns in domestic cats.
How Genes Determine Cat Colors
Genes tell our bodies how to make melanin, the pigment that colors hair. There are two kinds of melanin: eumelanin (black and dark brown) and pheomelanin (red and yellow). The way these melanins mix with genes decides a cat’s coat color.
Dominant vs. Recessive Color Traits
In cat color genetics, traits can be either dominant or recessive. For example, the gene for black coat color is dominant. On the other hand, the gene for orange is recessive but linked to sex. This knowledge helps predict different cat types by color in breeding.
Sex-Linked Color Inheritance
Some color traits, like orange, are sex-linked. This means the gene for this color is on the X chromosome. Female cats, with two X chromosomes, can carry different colors on each X, leading to tortoiseshell patterns. Male cats, with one X and one Y chromosome, show the color of their single X chromosome.
Exploring Cat Types by Color: A Comprehensive Overview
Exploring cat types by color reveals a wide range of hues and patterns and patterns. Each cat is unique. The world of cat colors is complex, involving genetics, breed characteristics, and environmental factors.
Primary Color Classifications
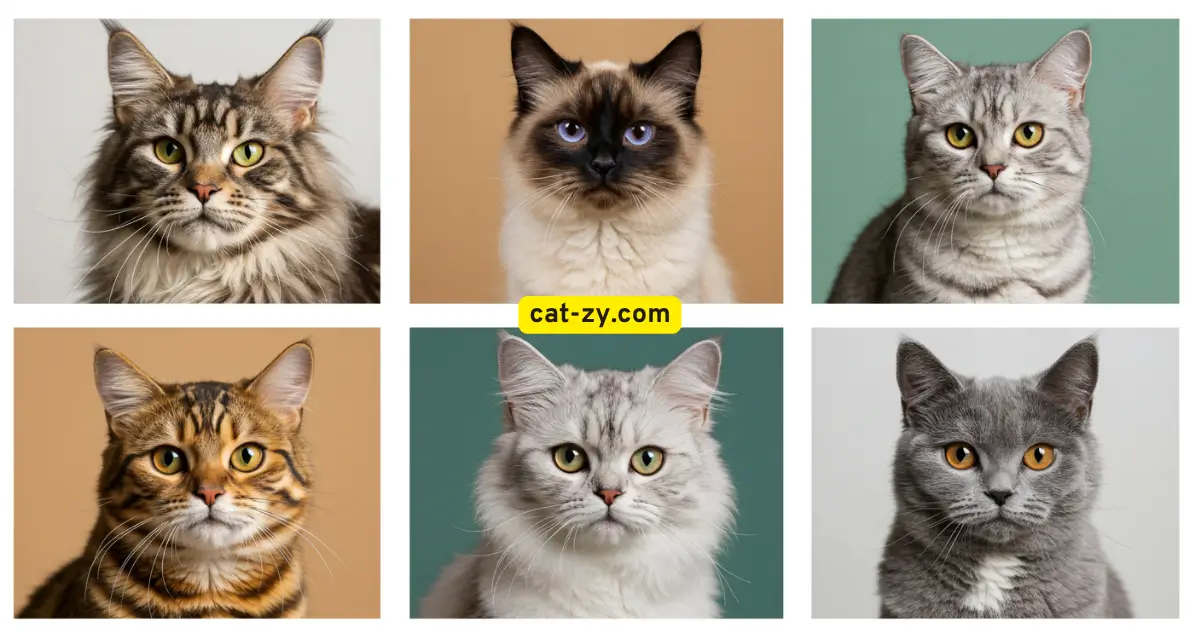
Cat types by color fall into primary categories. These include solid colors, tabby patterns, tortoiseshell, and calico. Solid colors range from pure white to deep black. They also include various shades of gray, blue, and red.
Understanding these cat types by color classifications helps with identification
Pattern vs. Base Color Distinctions
The difference between a cat’s pattern and base color is key. The base color is the cat’s overall color. The pattern shows how the color is distributed on the cat’s coat.
For example, a tabby cat has a base color with stripes or dots.
How Environment Affects Color Perception
Environmental factors, like sunlight, can change how a cat’s color is seen. Sunlight can fade or darken certain colors. It can also change the color’s intensity, especially in cats with lighter coats.
Knowing these factors helps you appreciate your cat’s unique color and what influences it.
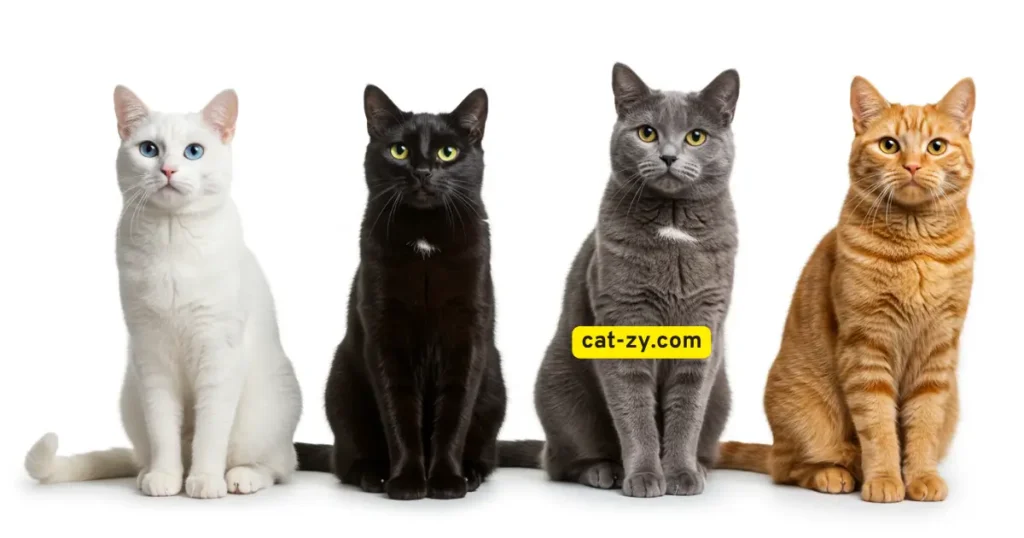
Solid-Colored Cats: From Midnight Black to Pure White
Among cat types by color, solid-colored cats are simple yet elegant. They come in black, white, gray, blue, red, and cream colors. Their coats are uniform, thanks to specific genetics.

Black Cats: Variations and Characteristics
Black cats are known for their mystery and elegance. Their solid black coat comes from lots of melanin. Variations in their coat can show up, like a brown or blue tint in certain light. But, they are mostly deep, rich black.
White Cats and Special Considerations
White cats lack melanin, making them white. But, they face special issues. They can get sun damage and might be more likely to have health problems like deafness, especially with blue eyes.
Gray, Blue, Red, and Cream Solid Varieties
There are more colors in solid cats, like gray, blue, red, and cream. Gray and blue cats get their color from diluted black pigment. Red and cream cats have a different genetic makeup that affects their phaeomelanin, a pigment for red and yellow.
Understanding these cat types by color and their genetics shows the beauty and diversity of solid-colored cats. Whether you like a sleek black cat or a unique red cat, each color has its own appeal.
Bi-Color Patterns: Tuxedos, Van Patterns, and More
Bi-color patterns represent fascinating cat types by color to study. You might know the classic tuxedo cat. But, bi-color patterns go way beyond that.
The colors on a bi-color cat’s coat are not just pretty. They come from special genetic mixes. Let’s explore the world of bi-color cats and their patterns.
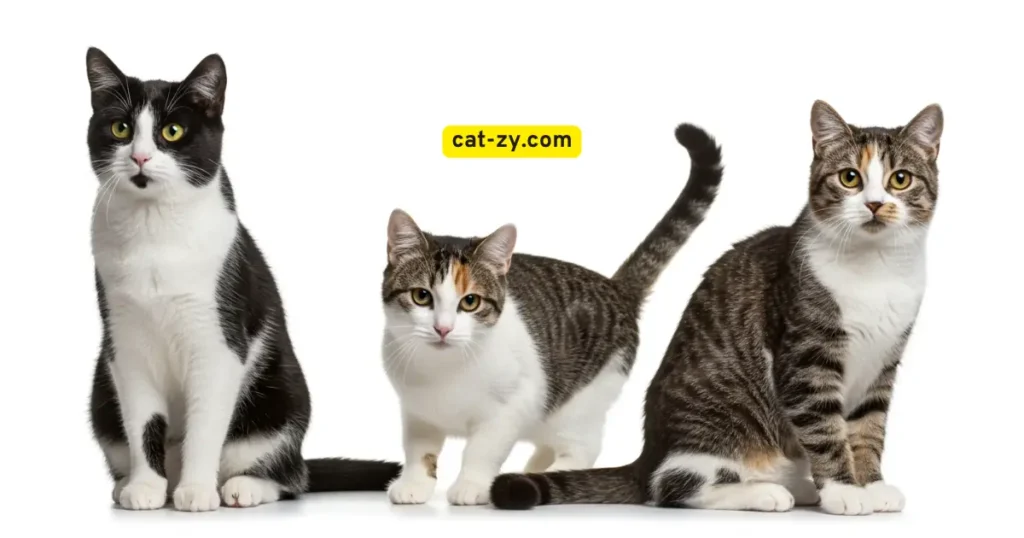

Classic Tuxedo Patterns
The tuxedo cat is well-known for its look. It has a black coat with white on the paws, belly, and face. This makes it look like it’s wearing a tuxedo.
Van and Bi-Color Variations
Van patterns show color on the head and tail, with a white body. Bi-color cats can have white with color patches or mostly color with white spots. The color mix can vary a lot.
Harlequin and Magpie Patterns
Harlequin cats have a mix of colors in a special pattern, mostly white. Magpie patterns are similar but can have more color variety. Both patterns are eye-catching and add to the variety of bi-color cats.
Learning about these cat types by color helps us appreciate feline diversity. It also gives us a peek into their genetics. Whether you love cats or just enjoy watching them, bi-color cats are fascinating.
Tabby Patterns: Decoding Nature’s Most Common Design
Tabby patterns showcase some of the most common cat types by color. From classic to mackerel and more, each pattern has its own special traits. This diversity makes tabby cats truly unique.
Classic (Blotched) Tabby Markings
The classic tabby pattern features broad, swirling designs on the cat’s fur. These patterns are often called “blotched.” The agouti gene causes this, creating a special M-shaped mark on the forehead.
Mackerel and Ticked Tabby Variations
The mackerel tabby has a striped look, with thin stripes on the body. The ticked tabby has a softer pattern. It looks like salt and pepper, without clear stripes or blotches.
Spotted Tabbies: Nature’s Leopards
Spotted tabbies have a leopard-like look, with spots instead of stripes. This unique pattern comes from genetic changes that affect how pigment is spread. It creates a special visual effect.
Learning about these tabby patterns helps us see the beauty and variety in cat coats. Whether you’re a cat breeder or just love cats, these cat types by color patterns are captivating. Its intricate designs are truly beautiful.
Point-Colored Cats: Siamese and Beyond
Point-colored breeds represent distinctive cat types by color? You’re not alone. Breeds like the Siamese and Himalayan are loved for their special looks. These cats have a lighter body coat with darker points on their extremities, face, and ears.
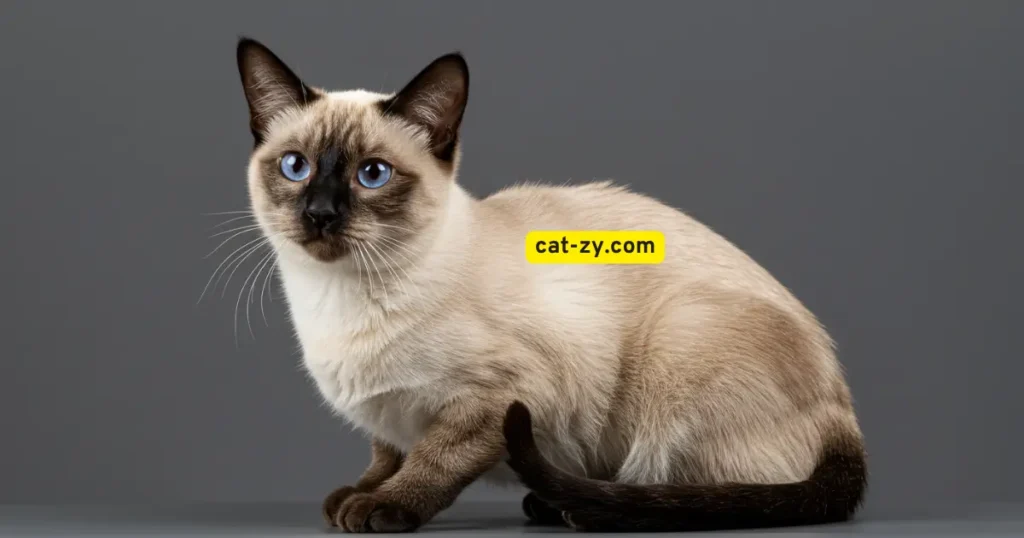

The genetics behind this coloration are fascinating. It’s due to a temperature-sensitive enzyme that affects melanin production. Melanin is the pigment that gives hair its color. This leads to the unique pattern seen in Siamese cats.
Siamese Coloration Explained
The Siamese breed is famous for its point coloration. Their coat pattern comes from a mutation in the tyrosinase enzyme. This enzyme is temperature-sensitive.
This means the cooler parts of their body (like extremities, face, and ears) produce more melanin. This results in a darker color.
Himalayan and Ragdoll Points
Other breeds, like the Himalayan and Ragdoll, also have point coloration. They share a similar coat pattern with the Siamese. But they look and act differently.
The Himalayan, for example, has a more compact body and a flatter face than the Siamese.
Temperature-Sensitive Albinism
Temperature-sensitive albinism isn’t just for cats; it’s also seen in animals like rabbits and mice. In cats, it causes the point coloration. Knowing about this genetic trait helps us appreciate the beauty of point-colored cats.
Tortoiseshell and Calico Patterns: The Colorful Mosaics
Among cat types by color, tortoiseshell and calico patterns are stunning. Each has its own look. These patterns have amazed cat lovers for a long time. They come from genetics.
Spotting the Difference
Tortoiseshell cats mix orange and non-orange colors in a marbled way. On the other hand, calico cats have white with orange and black patches. This makes them stand out.
Calico cats are known for their white base. This is what sets them apart from tortoiseshell cats.
The Genetics Behind These Female-Dominant Patterns
The science behind these patterns is interesting. They mostly show up in female cats. This is because of how genes work.
Female cats have two X chromosomes. This lets them mix colors. Male cats rarely show these patterns because they only have one X chromosome.
Dilute Versions and Variations
Dilute tortoiseshell and calico cats have softer colors. These colors can range from pale to soft blues and grays. This adds to their beauty and uniqueness.
Rare and Unusual Cat Color Patterns
Some cat types by color are so rare they’re considered extraordinary, they’re considered extraordinary. The amber and cinnamon colorations are among these. These colors not only make cats look amazing but also show how diverse felines can be. Exploring these colors reveals the interesting genetics behind them.
Chimera Cats: Two Cats in One
Chimera cats are a rare sight. They have two different cell populations, creating a striking mix of colors. This happens when two embryos merge during fetal development. You might notice a clear difference between the two colors, making these cats truly unique.
Smoke, Shaded, and Silver Patterns
Cats with smoke, shaded, and silver patterns have a mesmerizing coat color effect. The smoke pattern looks like a smoky haze over the base color. Shaded and silver cats sparkle because of how their color interacts with light. These patterns come from how melanin is made and the hair shaft’s structure.
The Elusive Amber and Cinnamon Colorations
The amber and cinnamon colors are among the rarest in cats. These warm, golden hues come from specific genetic variations. If you’re lucky enough to see a cat with these colors, you’ll find their beauty unique.
How Cat Colors Connect to Specific Breeds
Learning about cat colors and breeds can make you appreciate their diversity more. Cat breeds are known for their unique coat colors and patterns. These are set by breed-specific standards, which guide breeding practices.
Breed-Specific Color Standards
Registries like the International Cat Association (TICA) and the Cat Fanciers’ Association (CFA) create breed-specific color standards. These rules help keep breeds consistent and guide breeders. For example, the Siamese breed has a special point coloration due to a genetic factor.
Colors That Define Certain Breeds
Some breeds are famous for their colors. The British Shorthair is known for its blue-gray coat. The Ragdoll stands out with its pointed coat in many colors. These colors and patterns come from selective breeding and are key to the breed’s identity.
Controversial Color Breeding Practices
Some breeding for specific colors raises ethical questions. For instance, extreme coat colors can lead to health problems. Breeders should always put the health and well-being of cats first, not just their looks.
Identifying Your Cat’s Color Pattern: A Practical Guide
To figure out your cat’s color pattern, start by looking closely at its coat.
Key Features to Observe
First, check the color spread on your cat’s coat. See if it’s a solid color or if it has patterns like tabby, tortoiseshell, or bi-color. Look for any special markings or points.
Using Coat Length and Texture as Additional Clues
The length and feel of your cat’s fur can also give hints. Long-haired cats look different from short-haired ones because of their fur.
Tools and Resources for Pattern Identification
There are many online tools and breed guides to help you identify your cat’s color pattern. You can also get advice from a vet or a professional cat breeder.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Diversity of Feline Coloration
You now understand the complex world of cat types by color. The variety in feline coloration is amazing. Each cat is unique, with solid colors and intricate tabby patterns.
Appreciating cat colors is more than just looking good. It’s about understanding the genetics behind them. Recognizing different patterns and colors helps you connect with your cat. It shows their individuality.
As you learn more about cat colors, you’ll find it’s a rich topic. You’ll appreciate your cat’s unique traits and enjoy their colors.
FAQ
What determines a cat’s color pattern?
A cat’s color pattern comes from genetics. It’s about how genes work together to make melanin. This pigment decides the hair color.
Are certain cat colors more prone to health issues?
Yes, some cat colors face more health risks. White cats might be deaf because of their genetics. Cats without pigmentation around their eyes and ears could get skin cancer.
Can a cat’s color pattern change over time?
Yes, a cat’s color can change with age, environment, and health. For example, some cats get more defined points as they grow older.
How do I identify my cat’s color pattern?
To spot your cat’s color pattern, look at their coat’s color, pattern, and texture. You can also ask a vet or a certified cat breeder for help.
Are tortoiseshell cats always female?
Yes, most tortoiseshell cats are female. This is because the pattern’s genetics are linked to the X chromosome. Male tortoiseshells are rare, usually with an extra X chromosome (XXY).
What is the difference between a calico and a tortoiseshell cat?
Calico cats have a white coat with orange and black patches. Tortoiseshell cats have orange and black swirling, often with little white. The main difference is the white amount and color distribution.
Can cat colors be linked to specific breeds?
Yes, some cat colors and patterns are tied to certain breeds. For example, Siamese cats have point coloration. British Shorthairs often have solid colors.
How do environmental factors affect a cat’s color?
Environment, like sunlight, can change a cat’s color. Cats in direct sunlight might see their coat color fade or darken.